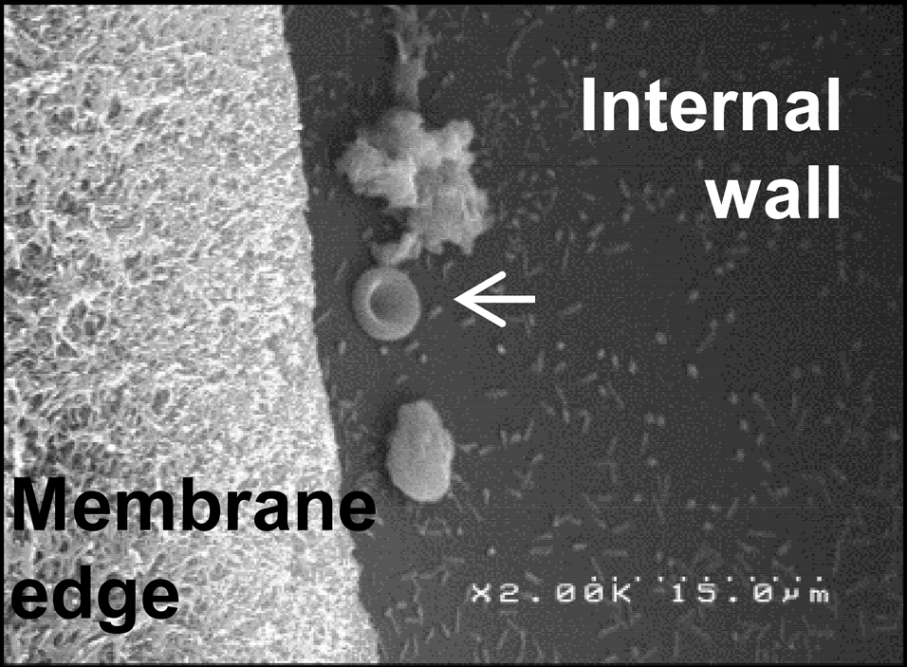
When patients reach the ultimate stage of chronic kidney disease, a renal replacement therapy (dialysis or renal transplantation) is required. In 2014, the incidence of end-stage renal disease (ESRD) was 163 new cases per million inhabitants in France. Each year, this incidence rate increases by 2 to 4%, this growth being mainly related to societal factors such as the increasing incidence of metabolic diseases (type II diabetes) or the aging of the population. The costs related to the management of end-stage renal disease have been estimated at more than 1.5 billion euros per year, which represents approximately 1% of the annual budget of the health insurance; dialysis being on average more expensive than renal transplantation. Although it is desirable for medical and economic reasons to perform transplantation as soon as possible, dialysis is often a mandatory step for ESRD patients. Dialysis can be associated with cardiovascular disturbances, blood pressure drops, and other discomforts. Research to improve dialysers and dialysis procedures in order to improve the performance and acceptability of treatment is therefore a major focus of development in nephrology.
The axis of experimental development is coordinated by Mr. Alain Ficheux and Dr Angel Argilés. The projects developed include :
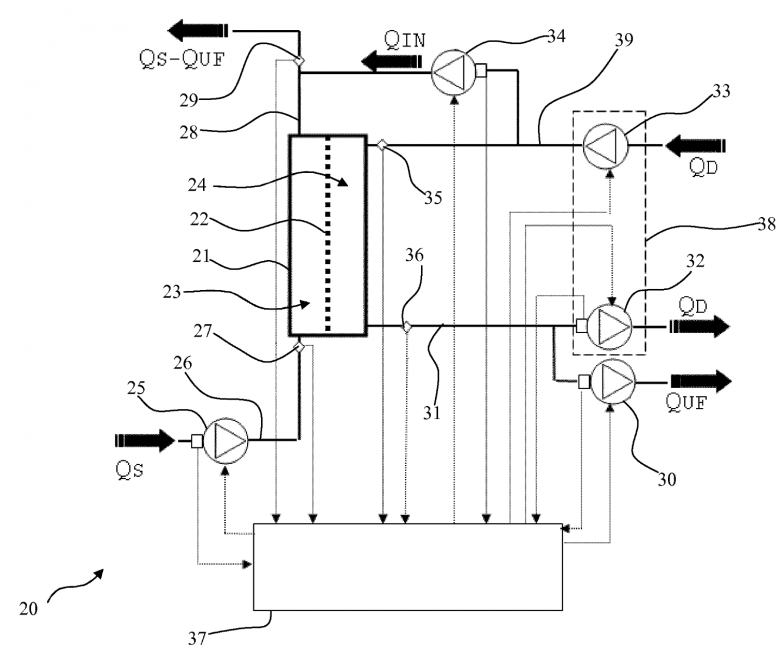
- Study of the dynamic hydrostatic pressures of the dialysis system
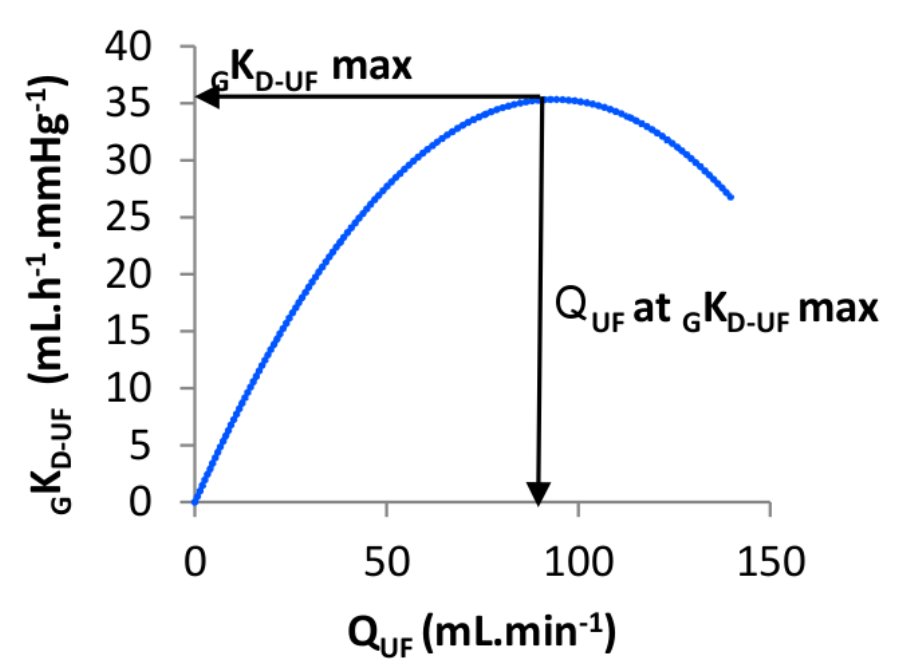
- Study of the overall ultrafiltration coefficient of the dialysis system (gKD-UF)
Techniques : prospective clinical studies, in vivo dialysis, in vitro dialysis